The world has gone through a progression of remarkable periods, each marked by significant innovations that have essentially affected the manner in which we live, work, and interact with our environmental variables. These phases, known as the Industrial Revolutions, have been propelled by mechanical headways that have reclassified firms, changed economies, and spurred cultural progress.
The First Industrial Revolution: A Pivotal Shift in Human History
The First Industrial Revolution, originating in Great Britain throughout the eighteenth hundred years, indicated a turning point in mankind’s set of experiences. It declared a groundbreaking movement from an agrarian, workmanship based economy to one characterised by motorized creation, mechanical development, and extraordinary monetary development.
- The Flash of Development: A Union of Variables
A few variables added to the development of the First Industrial Revolution in England. The nation had plentiful typical assets, including coal and iron, which encouraged the expansion of new firms. A steady globe of politics and an expanding populace supplied a fertile platform to monetary extension. Besides, a feeling of logical desire and mechanical improvement entered English society, encouraging a setting beneficial for earth-shattering creations.
- Mechanization Takes Center Stage: Steam Power and Textiles
The indication of the First Industrial Revolution was the progress from laborious work to mechanized creation. This change was highlighted by the advancement of steam power, a progressive innovation that harnessed the force of steam to drive hardware. James Watt’s steam motor, licensed in 1769, changed into a crucial power in changing undertakings, especially materials and transportation.
The material commerce, a pillar of the English economy, went through an emotional transformation throughout this period. Developments, for example, the turning jenny, the water outline, and the power loom improved the manufacture of yarn and material, completely expanding result and proficiency. These progressions established England’s standing as a worldwide forerunner in material assembling.
- Transportation: Interfacing a Country and a World
The effect of steam power stretched out past industrial buildings, disturbing transportation too. The advancement of steam-controlled trains, driven by George Stephenson’s Rocket in 1829, inaugurated the time of rail lines. This breakthrough significantly cut travel times and transportation prices, functioning with the expansion of products and persons across England and then some.
- The Expanding influence: Cultural Changes
The First Industrial Revolutions affect extended out a long ways past innovative headways, significantly modifying social designs, monetary frameworks, and metropolitan scenes. The ascent of production lines and modern focuses encouraged a flood in urbanization, as individuals went from rustic regions hunting for work potential open doors. This transition reshaped the social texture, generating new issues associated with dwelling, sterilizing, and general wellbeing.
- Decision: A Tradition of Development and Change
The Main Industrial Revolutions produced a permanent stamp on mankind’s set of experiences, creating way for ensuing Industrial Revolutions and molding the advanced world we possess today. It showcased human inventiveness and the breakthrough force of innovation, while likewise portraying the cultural issues that occur with speedy industrialization. The illustrations gathered from this time keep on illuminating our way to deal with technical advancement and cultural turn of events.
The Second Industrial Revolution: Electrifying the World
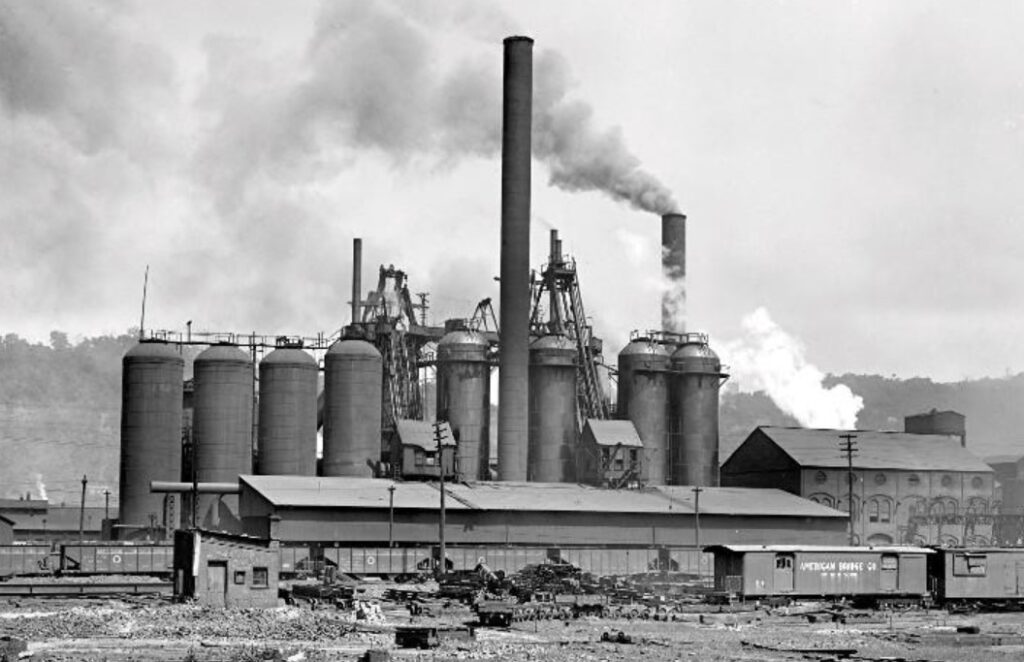

The Second Industrial Revolution, traversing the late nineteenth and mid twentieth hundreds of years, marked another age of innovative headways and cultural changes. At its center lay the saddling of power, a flexible energy source that reformed enterprises, reconfigured letters, and revolutionized normal daily existence.
- The Rise of Electricity: A New Era of Power
Power arose as a pioneering power during the Second Industrial Revolution, on a very basic level changing the manner in which firms worked and social orders worked. The advancement of generators and the foundation of force frameworks empowered the broad conveyance of power, filling a flood of improvements and uses.
- Lighting the World: Enlightening Homes and Urban communities
One of the most notable benefits of power was its capacity to brighten houses and urban neighborhoods, expanding the day and transforming day to day lives. The creation of the brilliant light by Thomas Edison in 1879 marked a crucial point, supplanting weak and dangerous gas lights with a more secure, more effective wellspring of light.
- Correspondence Re-imagined: Interfacing Across Distances
Power changed correspondence, facilitating the transport of data over huge distances with incredible speed and precision. The creation of the message during the nineteenth century modified substantial distance correspondence, while the improvement of the phone in 1876 by Alexander Graham Ringer affected individual correspondence.
- Mass Production and Assembly Lines: Reshaping Manufacturing
The Industrial Revolution saw a revolution in assembling, driven by the introduction of large-scale manufacturing methods and mechanical production equipment. Spearheaded by Henry Portage in the mid-twentieth 100 years, sequential construction techniques considered the proficient manufacture of standardized products, entirely enhancing results and minimizing charges.
- The Automobile: A Symbol of Innovation and Mobility
The car evolved as a distinguishing image of the Second Industrial Revolution. The improvement of the gas-powered engine revolutionized transportation, delivering a speedier, more adaptable method of movement contrasted with horse-drawn carriages or railroads. The wide-scale manufacturing of vehicles, embodied by Portage’s Model T, made vehicle proprietorship open to a more extensive fraction of society.
- Cultural Changes: Urbanization and New Difficulties
The Second Industrial Revolution achieved tremendous cultural changes, speeding up urbanization and introducing new obstacles. The growth of manufacturing plants and modern focuses pulled in vast quantities of individuals to urban regions, prompting swift metropolitan extension and the establishment of new friendly elements.
- Decision: A Tradition of Development and Cultural Change
The Second Industrial Revolutions left an enduring bequest, altering the cutting edge world and laying the framework for following mechanical headways. The outfitting of power transformed undertakings, modified correspondence, and reshaped day-to-day existence. The cultural modifications produced by this period keep on impacting comprehension we might view urbanization, work, and the effect of innovation on society.
The Third Industrial Revolution: Ushering in the Digital Age

The Third Industrial Revolution, starting in the last 50% of the twentieth 100 years, marked a remarkable trend towards a computerized society. This epoch saw the ascent of PCs, the web, and robotization, disturbing firms, reclassifying correspondence, and changing the global economy.
- The Digital Revolution: Computers and Information Technology
The advent of PCs and the advancement of data innovation (IT) sat at the center of the Third Industrial Revolution. These advances transformed how data was handled, stored away, and got, driving a flood in efficiency and proficiency throughout enterprises.
- Automation and Robotics: Reshaping Manufacturing and Production
Automation and robotics arose as significant drivers of advancement during the Third Industrial Revolution. The presentation of mechanized frameworks and mechanical improvements in assembling reformed creative processes, empowering expanded correctness, consistency, and results.
- The Internet: Connecting the World and Transforming Communication
The improvement of the web marked an urgent second in the Third Industrial Revolution. This worldwide organization of networked PCs changed correspondence, powerful occasions, and consistent sharing of info across large distances. The web affected how individuals linked, got to date, and directed business, in a general sense transforming the social and financial scene.
- The Rise of the Information Age: Knowledge and Data at the Forefront
The Third Industrial Revolution introduced the Data Age, when knowledge and information turned out to be progressively crucial resources. The capacity to obtain, investigate, and employ information truly developed into a critical predictor of growth in different firms, prompting the rise of information-driven direction and the improvement of new fields like information science.
- Globalization: An Associated World Economy
The Third Industrial Revolution sped up globalization, cultivating more notable monetary connectivity and dependency among countries. The web and headways in correspondence advancements worked with cross-line exchange and cooperation, empowering organizations to function on a worldwide scale.
- Cultural Changes: The Advanced Gap and New Difficulties
The Third Industrial Revolutions achieved significant cultural alterations, creating new challenges and featuring the relevance of advanced competence and admittance to innovation. The computerized partition, the hole between those with and without admittance to sophisticated innovations, appeared as a basic concern, impacting monetary open doors and social incorporation.
- Determination: A Tradition of Computerized Change
The Third Industrial Revolution left a huge heritage, bringing the electronic age and transforming how we live, work, and communicate. The ascension of PCs, the web, and computerization disturbed businesses, redefined correspondence, and transformed the worldwide economy. The cultural alterations gained by this time keep on molding how we can view the advanced gap, the effect of innovation on business, and the job of information in the public arena.
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution: A Union of Innovations
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, the epoch we are as of now confronting, is characterised by the confluence of physical, advanced, and natural spaces. This mix of improvements is concealing the limitations between the genuine and virtual universes, prompting groundbreaking adjustments in ventures, societal orders, and our grasp of human life.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Emulating Human Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is at the very vanguard of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, empowering computers to replicate human intellect and execute errands that were traditionally considered as selected by people. Simulated intelligence is revolutionizing initiatives like medical care, money, and transportation, with applications spanning from clinical discoveries to independent cars.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting the Physical World
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the manner in which we collaborate with physical goods. By implanting sensors and availability into everyday gadgets, the IoT is building an organization of networked gadgets that can gather, trade, and break down information. This interconnectedness is empowering smart houses, savvy urban neighborhoods, and an extra responsive and proficient world.
- Advanced Robotics: Redefining Human-Machine Interaction
Advanced Robotics is obscuring the distinctions between people and machines. Robots are growing out to be progressively modern, suited for accomplishing intricate tasks with accuracy and flexibility. Cooperative robots, or cobots, are working near by people in diverse organizations, enhancing efficiency and wellbeing.
- Biological Technologies: Reshaping Medical Care and Human Potential
Progresses in biotechnology, including quality modifying and produced science, are redefining medical treatment and bringing up serious moral dilemmas. These advances hold the opportunity to repair infections, boost human capacities, and change how we might perceive existence itself.
- Impact on Industries: Disturbance and Change
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is troubling firms across the range, from assembling to medical care to return. Customary plans of action are being tried, and new open doors are appearing as innovation reshapes how items and administrations are manufactured, conveyed, and consumed.
- Cultural Changes: Moral Contemplations and Human Effect
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is bringing up fundamental cultural questions about the eventual fate of employment, the effect of innovation on human connections, and the moral repercussions of headways in simulated intelligence and biotechnology. Guaranteeing that these innovations are generated and utilized dependably is a basic test confronting humankind.
- End: Exploring the Future with Obligation
The Fourth Industrial Revolutions brings both vast open doors and crucial difficulties. As we explore this amazing moment, it is necessary to embrace the power of innovation while caring to its moral and cultural repercussions. By encouraging cooperation, advancing computerized proficiency, and focusing on human values, we may design a future where innovation increases human prosperity and adds to a more unbiased, economical, and wealthy society.
The Industrial Revolutions: Shaping the Course of Society
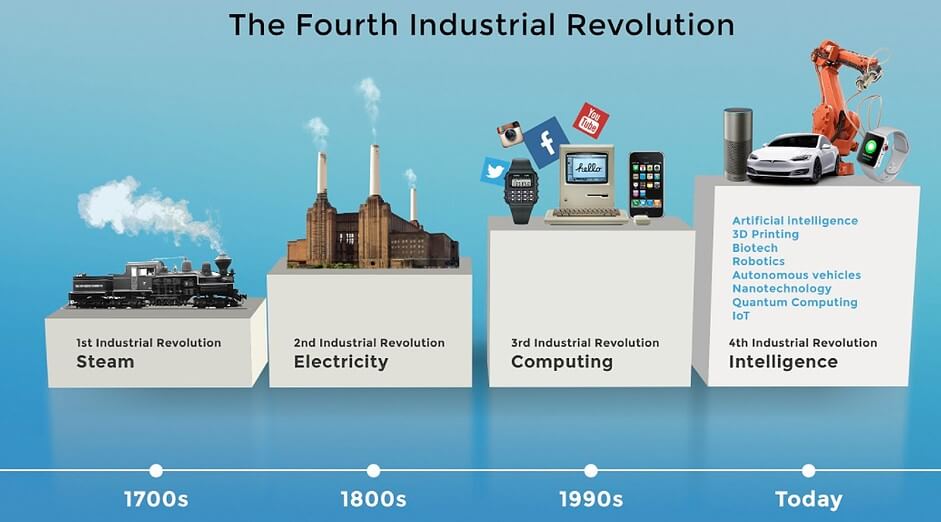
The Industrial Revolutions, a succession of remarkable periods set apart by innovative headways and cultural disruptions, have considerably molded the course of mankind’s set of experiences. These revolutions have upset firms and economies as well as generally affected societal designs, everyday settings, and the connection between people and innovation.
- Financial Changes: Expanded Efficiency and Abundance Creation
The Industrial Revolutions caused major financial developments, pushing improved efficiency, abundance creation, and worldwide exchange. The motorization of creation, the tackling of new energy sources, and the improvement of inventive technologies have revolutionized enterprises, empowering the large-scale manufacturing of labor and products at a cheaper cost.
- Urbanization: The Rise of Cities and New Social Dynamics
The Industrial Revolutions have spurred urbanization, as individuals transferred from provincial regions to metropolitan areas hunting for business open doors in processing plants and modern focuses. This fast urbanization led the growth of urban regions, making new welcoming features, issues in lodging and disinfection, and the formation of distinct metropolitan societies.
- Living Standards: Upgrades and Imbalances
The Industrial Revolutions have added to upgrades in expectations for everyday conveniences for some, offering access to a more substantial scope of products, administrations, and medical care progressions. In any way, they have moreover increased disparities, with abundance often focused among the people who own or control the method for creation, while laborers, especially in the initial periods of industrialization, confronted terrible working situations and inadequate incomes.
- Labor and Employment: Changing Elements and Difficulties
The Industrial Revolutions have modified job and business designs, moving from customary agrarian and craftsmanship-based labor to production line-based work and, all the more as of late, to information-based and administration-situated roles. These progressions have reached new obstacles, including position displacement because of computerization, the demand for reskilling and upskilling, and worries over laborer well-being and privileges.
- Social Developments and Changes: Tending to Imbalances and Further Developing Circumstances
The Industrial Revolutions have led to social developments and adjustments geared toward tending to the inequities and problems achieved by fast industrialization. Worker’s associations formed to campaign for laborers’ privileges, while social reformers lobbied for work on working situations, improved lodging, and entrance to schooling and medical facilities.
- Environmental Effect: A Developing Concern
The Industrial Revolutions significantly changed the climate, with contamination, asset consumption, and environmental change becoming the key challenges. The usage of non-renewable energy sources, the extraction of normal assets, and the age of modern trash have added to ecological debasement, featuring the necessity for economical practices and natural assurance methods.
All in all, the Industrial Revolutions have been a progression of groundbreaking periods that have profoundly influenced the trajectory of mankind’s collection of experiences. Every revolution has been characterised by earth-shattering innovations that have transformed firms, reshaped economies, and spurred cultural advancement.
The First Industrial Revolutions, set apart by the rise of steam power and motorization, revolutionized assembly and transportation. The Second Industrial Revolution saddled power, spurring large-scale industry and headways in correspondence. The Third Industrial Revolutions introduced the computerized age with PCs, the web, and mechanization. Furthermore, now, we stand at the edge of the Fourth Industrial Revolutions, characterised by the union of physical, technological, and organic spaces.
These revolutions have accomplished both tremendous advantages and serious obstacles. They have spurred monetary progress, worked on expectations for everyday luxuries for the vast majority, and disrupted enterprises. Nonetheless, they have also exacerbated inequities, modified work aspects, and elevated ecological problems.
As we explore the Fourth Industrial Revolution, it is vital to embrace the capability of innovation while tending to its moral and cultural repercussions. By promoting combined work, developing computerized proficiency, and focusing on human values, we may design a future where innovation enhances human prosperity and adds to a more fair, reasonable, and prosperous society.
Key takeaways:
The Industrial Revolutions have been remarkable periods fueled by mechanical headways.
Every Revolutions has transformed enterprises, reshaped economies, and stimulated cultural transformations.
The Industrial Revolutions offered two advantages and issues, including monetary development, working on expectations for everyday luxuries, imbalances, work adjustments, and ecological worries.
Exploring the Fourth Industrial Revolutions necessitates offsetting inventive advancement with social responsibilities.
By comprehending the effect of the Industrial Revolutions, we may more quickly plan for the obstacles and open opportunities that lie ahead.

quia nesciunt corrupti doloremque facere quo non nam. dolorum corrupti nisi amet eveniet repudiandae hic saepe sunt non provident minima. eos magni ea enim vel vitae repellat voluptatibus sed eum et a